
T accounts assist in budgeting and financial planning by tracking expenses, revenues, and other financial activities. Individuals and organizations can use T accounts to compare actual financial performance again. Accounting software can now integrate with your bank accounts and other financial systems, providing real-time transaction data. Likewise, create T-accounts for different expense categories like rent, utilities, or retained earnings charitable donations. This simplifies the process of gathering and recording tax-relevant information.
Special Considerations in Debit and Credit Accounting
- Manually maintaining T-accounts for every transaction can be impractical for large organisations with thousands of entries.
- Identifying the type of transaction – like buying supplies, paying rent, or earning revenue – is crucial for accurate recording.
- A debit is an entry made on the left side of an account, while a credit is an entry made on the right side of an account.
- Once you master these steps, T-accounts become a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding your business transactions.
For example, when a company sells goods on credit, the revenue account is credited, and the accounts receivable account is debited. In accounting, debit and credit are two fundamental terms that are used to record financial transactions. A debit is an entry made on the left side of an account, while a credit is an entry made on the right side of an account. The terms are used to indicate the increase or decrease in an account’s balance.

Bank Account
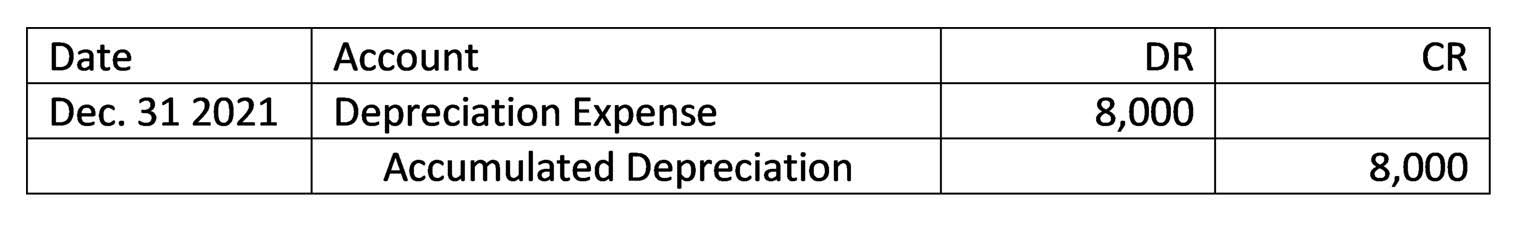
They help you track cash flow, analyze expenses, and ensure all your financial ducks are in a row. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different scenarios – the more you practice, the more confident you’ll become in managing your financial data. The following T-account examples provide an outline of the most common T-accounts.

Examples of T-Account
A T-chart is a tool used by accountants to record financial transactions. It helps to ensure that every transaction is recorded accurately and in the correct account. Accountants must use the T-chart correctly to ensure the accuracy of the general ledger and financial statements. In accounting, liability accounts are used to record debts or obligations that a company owes to others. Asset accounts are a vital component of any company’s financial health.


That’s why we’ve only gathered some of the most frequent financial activities businesses deal with in their day-to-day operating cycle. Because T accounts are posted into the General Ledger of a business, they’re also commonly recognized as ledger accounts. Imagine a conglomerate with numerous subsidiaries operating in t accounts diverse industries. Each subsidiary’s transactions require separate T-accounts, leading to a cluttered and cumbersome accounting system.
- Examples of debit transactions include cash purchases, payments made to suppliers, and payments made to employees.
- Due to its simplistic nature, T-accounts are also used as a learning tool to practice transactions and double-entry accounting.
- T-accounts may fail to capture the full picture in business scenarios involving multiple accounts and numerous transactions.
- Each account has its T account to record transactions specific to that account.
- Once journal entries are made in the general journal or subsidiary journals, they must be posted and transferred to the T-accounts or ledger accounts.
- In summary, debits and credits are essential tools for recording business transactions in an accounting system.
- Then, the journal entry is moved into the ledger, in the form of a T account.
Double-Entry Accounting
Some accounts have a debit-side balance, while others have a credit-side balance. That makes T accounts a good place to start when thinking about bookkeeping and accounting, but also financial management. For a lot of people, the balance sheet is one of the hardest financial statements to get to grips with. Year-over-year (YOY) is a financial term used to compare data for a specific period of time with the corresponding period from the previous… Instead, ledgers and automated systems handle transaction tracking.
As I owe both this month and last month’s rent, I have to pay £4000. My bank account is credited £4000, whilst the accounts payable account is debited £2000 and rent is debited £2000. Therefore, both debits and bookkeeping and payroll services credits are equal in this transaction. T accounts are a visual representation of an account in double-entry bookkeeping.